Atom:66z-Va2llq0= Lithium stands at the forefront of contemporary technological advancements due to its remarkable properties such as low density and high electrochemical potential. Its pivotal role in powering electric vehicles and renewable energy storage systems cannot be overstated. However, the environmental ramifications of lithium extraction raise significant concerns about sustainability and ecological integrity. As the demand for lithium continues to soar, exploring innovative approaches to mitigate these challenges becomes imperative. What strategies might emerge to balance our technological aspirations with environmental responsibilities?
Overview of Lithium’s Properties
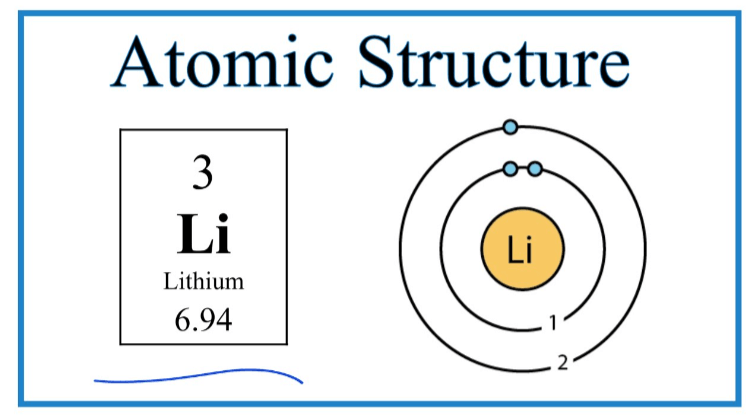
Lithium, a lightweight alkali metal characterized by its low density and high electrochemical potential, exhibits a unique set of properties that distinguish it from other elements in the periodic table.
Its physical properties include a silvery appearance and a melting point of 180.5°C, while its chemical properties showcase reactivity with water and oxygen, forming hydroxides and oxides, respectively, thus enabling diverse interactions within various environments.
Applications in Modern Technology
The unique properties of lithium, particularly its lightweight nature and high electrochemical potential, have positioned it as a key component in various modern technological applications.
Notably, lithium ion batteries dominate portable electronics and electric vehicles due to their efficiency and energy density.
Additionally, advancements in lithium extraction techniques enable sustainable sourcing, further enhancing lithium’s role in supporting innovative technologies and meeting global energy demands.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
How does the extraction and utilization of lithium influence environmental sustainability?
Lithium extraction significantly impacts ecosystems, often resulting in water depletion and habitat destruction.
To mitigate these effects, innovative recycling methods are essential, allowing for the recovery of lithium from used batteries, thus reducing the demand for raw materials.
Sustainable practices in lithium sourcing and recycling are critical for minimizing ecological footprints and promoting environmental resilience.
Read Also Carbon (C): 1sh2si2pj H = I = J
Future Trends in Lithium Usage
As the demand for electric vehicles and renewable energy storage solutions continues to escalate, the future landscape of lithium usage is poised for transformative developments.
Advances in lithium mining techniques, coupled with innovative recycling technologies, will enhance resource efficiency and sustainability.
This dual approach is essential for meeting the increasing global energy demands while minimizing environmental impacts, ultimately fostering a more liberated energy future.
Conclusion
In summation, Atom:66z-Va2llq0= Lithium properties render it indispensable in contemporary technological applications, particularly in energy storage systems. However, the environmental ramifications associated with its extraction necessitate a reevaluation of current practices. The imperative for innovative recycling methods and sustainable sourcing strategies aligns with the burgeoning demand for electric vehicles and renewable energy solutions. As society advances further into the electric age, the stewardship of lithium resources will be paramount to ensuring ecological balance and technological progress.